Burnout Prediction Using Machine Learning
Technologies Used
Python, HTML, CSSMachine Learning (CatBoost, XGBoost, Gradient Boosting and LLM models)
Deep Learning (TensorFlow)
Python Libraries (pandas, streamlit, joblib, shap, numpy, openai)
PI Development (Flask)
Cloud Services (Google, Dockers)
Employee burnout has become a critical issue in modern workplaces, leading to decreased productivity, increased absenteeism, and higher turnover rates. In this project, we leverage data science techniques to predict burnout risk and provide actionable insights for businesses.
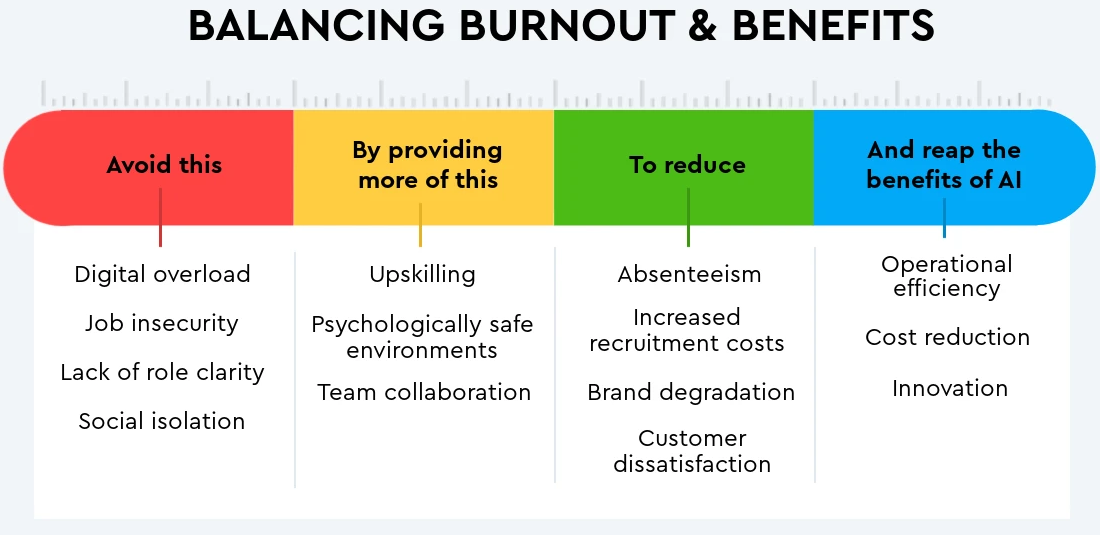
Dataset & Exploratory Data Analysis
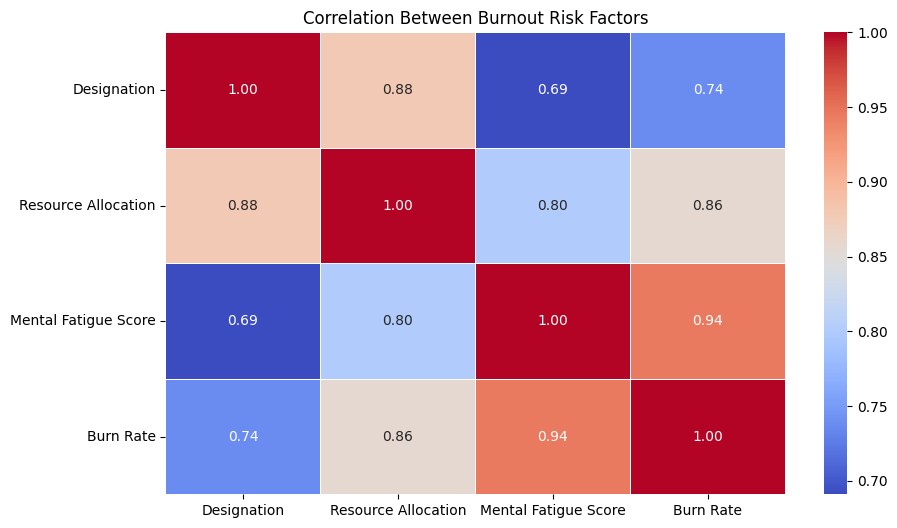
We analyzed a dataset containing information on employee workload, stress levels, salary fairness, and work-life balance. The dataset consists of 35,000 records and includes features such as:
- Gender, Work From Home option, tompany type
- Level of the job function (1-5)
- Level resources available to work (1-10)
- Remote Work Percentage
- Mental Fatigue Score (hurs worked without break, Difficulty concentrating, and sleep issues)
- target: Burnout Score (0-1 Scale)
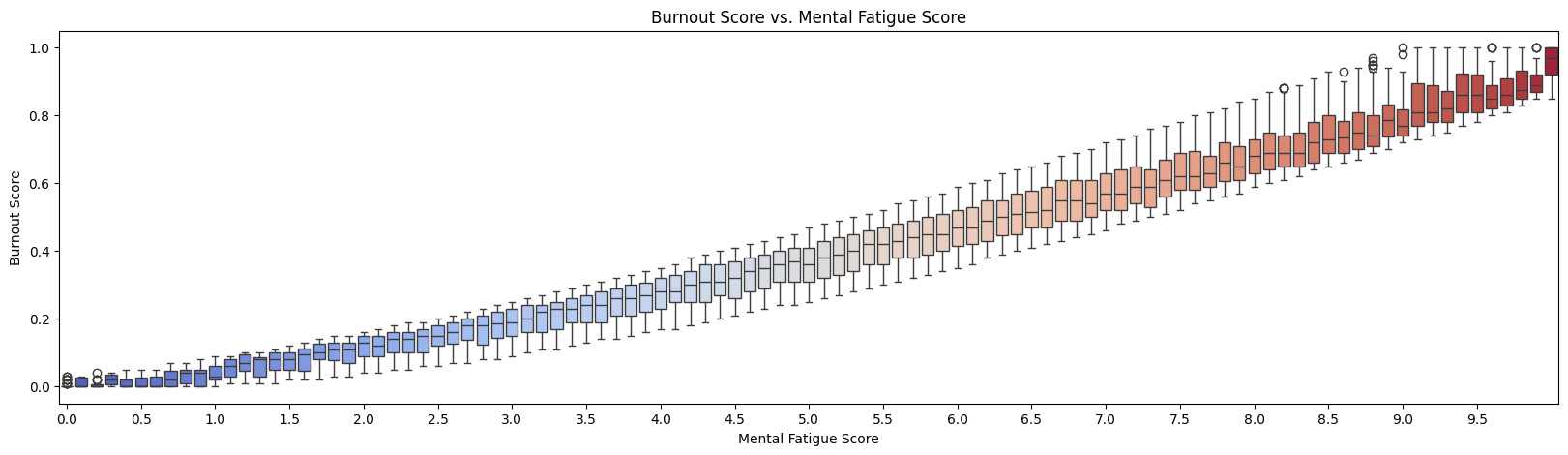
Key Insights from EDA:
- 85% of employees with burnout work more than 45 hours per week.
- 67% of employees experiencing burnout feel underpaid.
- Low remote work flexibility increases mental fatigue by 30%.
Machine Learning Approach
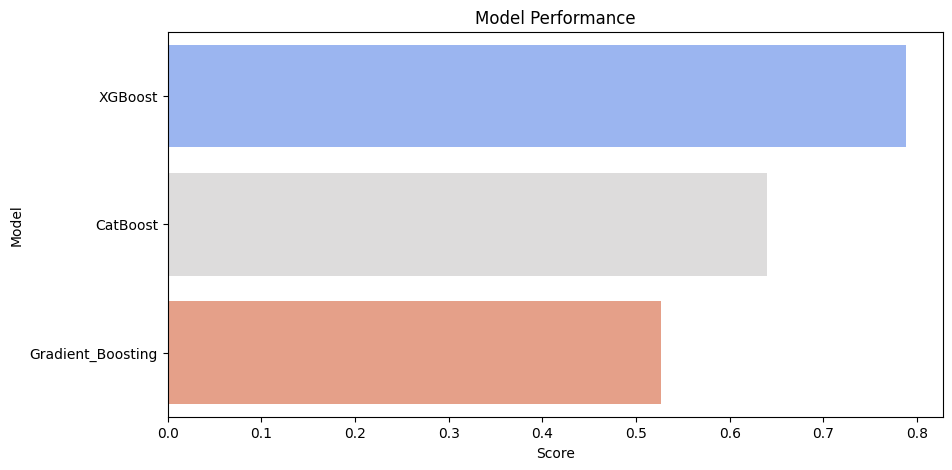
To predict burnout, we implemented several models and evaluated their performance:
- Gradient Boost - Baseline model for feature importance analysis.
- XGBoost - Best performer with 89% accuracy.
- Neural Networks (MLP) - Tested but easely overfiting. Used for deep learning-based predictions.
Future Development & Next Steps
Moving forward, we plan to enhance the project by:
- Integrating real-time employee data for continuous monitoring.
- Developing an API for HR teams to assess burnout risk dynamically.
- Expanding the dataset to include multi-industry insights.
- Refining model accuracy with deep learning architectures.
This project demonstrates how AI-driven insights can empower businesses to support employee well-being and optimize workforce efficiency.

